-
Ultimate Guide to Google Block Breaker Tools and Techniques

There’s a moment every digital professional knows too well.You’re researching, auditing, scraping, testing, or analyzing — and suddenly… blocked. CAPTCHA walls. Access denied. Rate limits. IP bans. This is where the concept of a google block breaker quietly enters the conversation. Not as a hack.Not as a shortcut.But as a strategy. This guide is written
-
Where to Buy Google Pixel 9 Fold Pro Online: Your Ultimate Guide

The tech world is buzzing again, and this time it’s all about foldable smartphones. Google has raised the stakes with its latest marvel: the Pixel 9 Fold Pro. Sleek, futuristic, and impossibly versatile, this device isn’t just another smartphone—it’s a glimpse into the future of mobile technology. But if you’re reading this, chances are you’re
-
E-Commerce Website Development by Garage2Global: Features, Benefits & Process

A few years ago, launching an online store felt simple. Pick a template, upload products, connect a payment gateway, and hope for the best. Today, that approach barely survives. Customers expect speed, trust, personalization, and seamless experiences across devices. Search engines demand structure and performance. Payment providers demand security. And business owners? They want sales,
-
UX Design Tactics Used in the Svedka 100 Proof Vodka Brand Website

Some brand websites shout. Others whisper. A few know exactly when to do both. The svedka 100 proof vodka brand website sits firmly in the third category. It doesn’t overwhelm visitors with endless menus or pushy calls to action. Instead, it guides, teases, and immerses—quietly confident in what it’s selling and who it’s selling to.
-
Free Undress AI Remover Tool: Ethical Issues and Online Safety Guide

The first time I heard someone mention a free undress AI remover tool, it wasn’t in a tech forum or a research paper. It was in a private chat. Quiet. Uneasy. Followed by a simple line: “Is this even legal?” That question sits at the heart of this entire conversation. AI image manipulation has moved
-
AI Avatar Solutions to Level Up Your Virtual Event Hosting

Virtual events didn’t fail because of technology. They failed because they felt empty. The early days of online conferences, webinars, and digital expos taught us a hard lesson: people don’t engage with platforms—they engage with presence. Eye contact. Voice. Personality. A sense that someone real is on the other side of the screen. That’s exactly
-
Keyword Optimization by Garage2Global Strategy in 2025

If you’ve been paying attention to SEO trends lately, you’ve probably noticed a quiet shift happening beneath all the usual noise. Marketers aren’t just chasing keywords anymore — they’re chasing intent, micro-topics, audience psychology, and real search behavior. And somewhere inside that shift, almost out of nowhere, keyword optimization by Garage2Global keeps popping up in
-
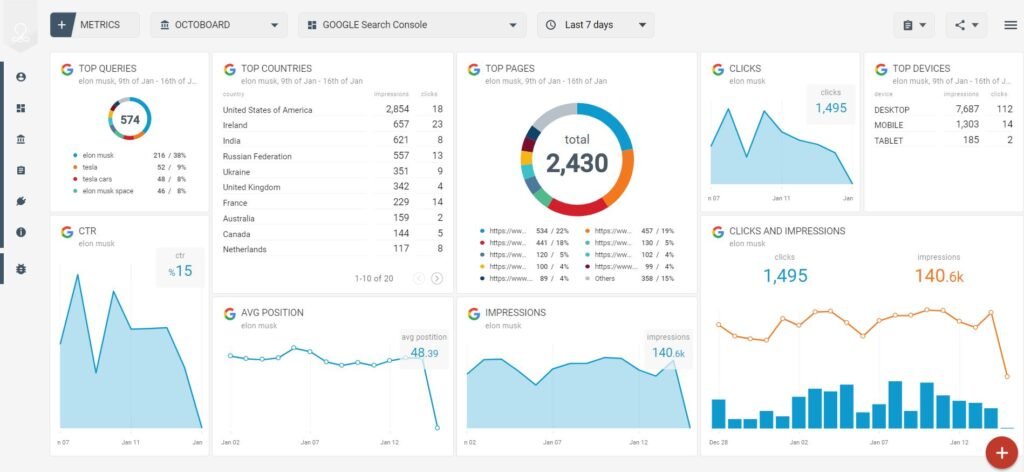
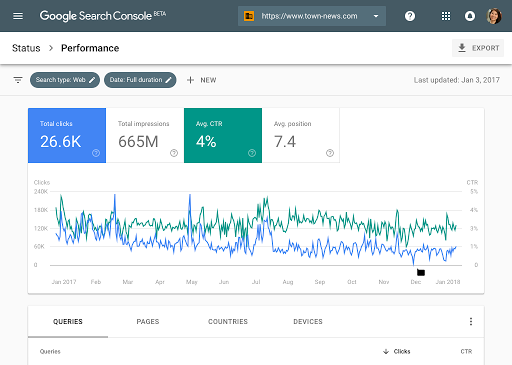
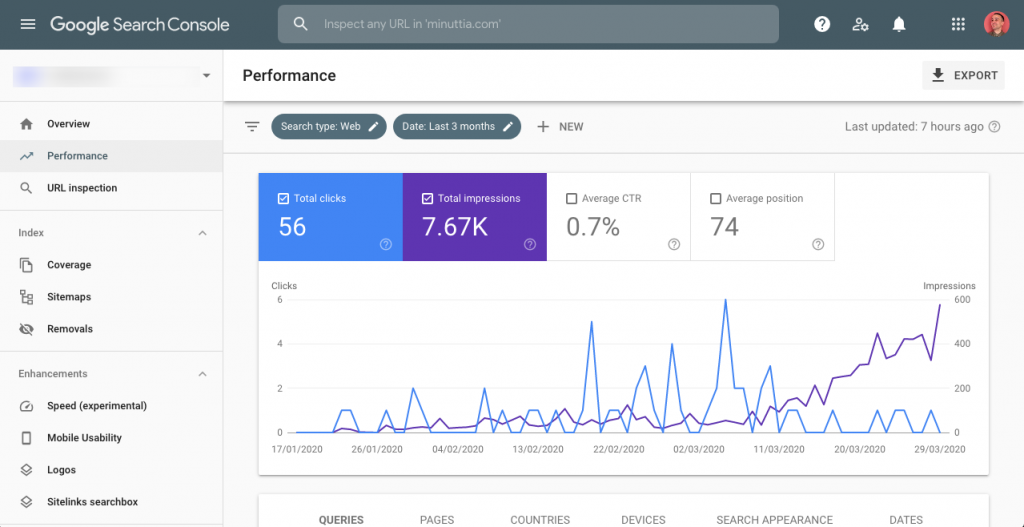
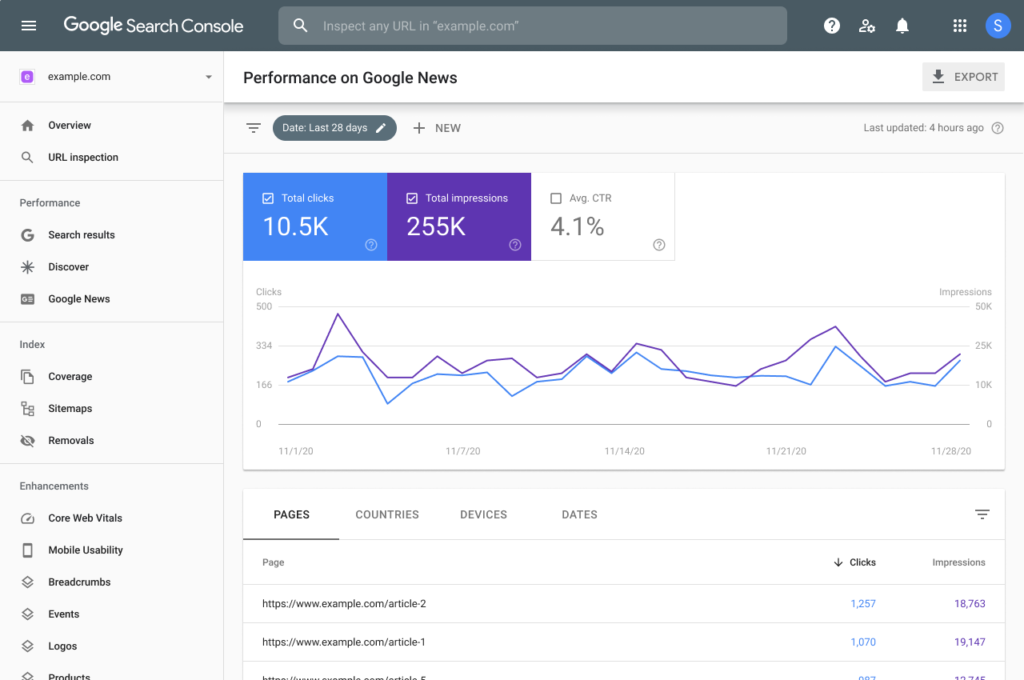
A Complete Guide to How ai seo tools scale agile solutions in 2025

In 2025, digital teams move faster than ever before. Search engines evolve weekly, customer expectations shift overnight, and product cycles have become so compressed that agility is no longer a luxury—it’s survival. Yet many teams hit the same wall: scaling. Scaling content, scaling workflows, scaling search visibility, and scaling team coordination. Somewhere in this growing
-
Classroom Essential: Heveer Foundations Basic Keywords Poster K-1-2

Walk into any vibrant early-grade classroom and you’ll notice a pattern: the walls speak long before the teacher does. Colorful charts, alphabet strips, number lines — all of them quietly guiding young learners through the noise and mystery of their first school years. But among all the visual tools teachers rely on, one item has
-
How to Use Keywords Research Pro to Uncover Hidden Ranking Opportunities

Every SEO strategist has experienced that familiar moment: staring at a blank screen, exhausted from digging through a dozen keyword tools that all seem to show the same predictable terms. It’s like trying to find treasure on a beach that’s already been searched by everyone before you. And then you try keywords research pro—a tool
Search
About
MWT Media Blog brings you the latest SEO news, market trends, and actionable insights to help brands, marketers, and publishers stay ahead in a fast-changing digital landscape. From algorithm updates to outreach strategies, we break down what really matters.
Stay updated with SEO news, trends, and insights shaping the digital marketing world. Practical updates, real strategies, and market-focused analysis—no fluff.
Categories
Tags
Gallery